For example, it may be stipulated in the credit management policy that the credit limit granted to customers shall not exceed xx% of tangible net worth.
Indeed, the TNW meets the obvious need, but not so easy to get, to know the intrinsic value of a company based on what is material, ie that can be converted into cash in case termination of the activity and of liquidation of assets (sale of fixed assets, inventory and payment of receivable) and the payment of debts with third parties (banks, suppliers, taxes ... etc..).
TNW is a concept very down to earth. All intangible valuations, ie intangible assets: patents, expenses, goodwill, licenses and all other intellectual property that the company may have are excluded in the calculation.
Tangible Net Worth calculation
As a key prerequisite to any assessment of TNW, it is necessary to ensure that the balance sheet is representative of the financial reality of the business. If this is not the case and financial statements are fraudulent, the TNW will be biased and lead to a false estimate of the value of the company.For example, if the value of the stock is overvalued (valuation in the balance sheet of dead stock), tangible net worth will also be false (see the pitfalls the of balance sheet). This principle is true for any difference in value of balance sheet assets (fixed assets, receivables ... etc..) compared to reality.
Why exclude intangibles from credit analysis
Intangible assets are immaterial and unquantifiable (cash is intangible but perfectly quantifiable), they are subject to subjectivity in large proportions. Indeed, how to define rationally the value of goodwill or a patent? It is extremely difficult because their actual value depends on external context which may rapidly evoluate.For example, a patent may have some value for a few months and become obsolete overnight. The value of goodwill may vary depending on many criteria: competitive environment, market growth, positioning.
Consequence of this subjectivity, the valuation of intangible assets varies with the business strategy. They will swell if the executive wants to sell his company, they will decrease if it wants to reduce its net income.
Moreover, the principle of credit analysis is to determine the capacity of a company to pay its bills in a few months. However, intangible assets are hardly marketable and therefore does not strengthen the solvency of a company in the short term.
 The principle of tangible net worth is not to deny the intangible assets of a company which are, in most cases, a reality, but to put them aside because they do not help the company meet its debts .
The principle of tangible net worth is not to deny the intangible assets of a company which are, in most cases, a reality, but to put them aside because they do not help the company meet its debts .TNW calculation method
Total assets - intangible assets - total of debts to third parties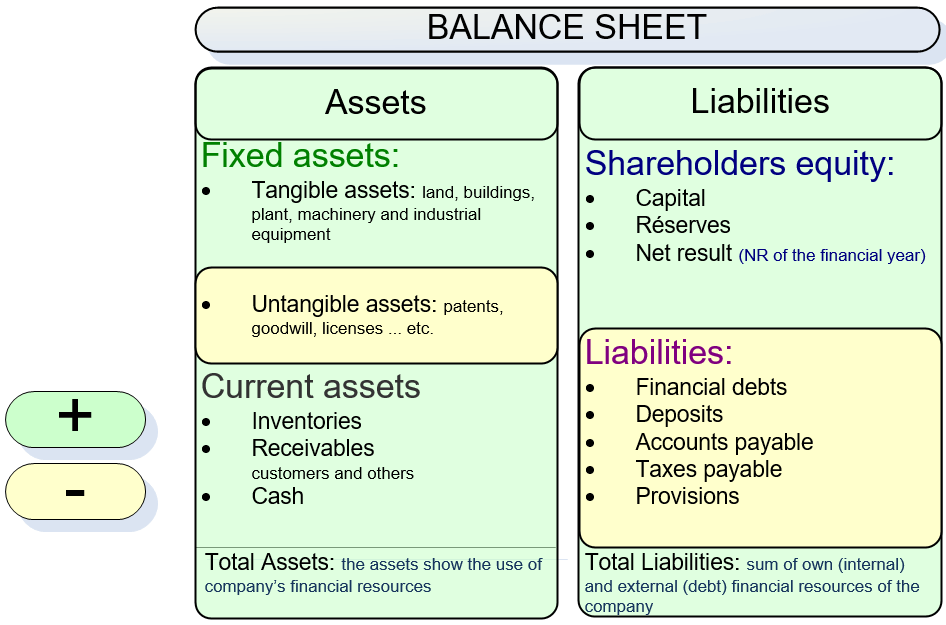
Credit analysis and Tangible Net Worth
What to do once TNW is calculated?First, the TNW is not enough to achieve a solid financial analysis. Many other factors must be taken into account when looking to the income statement and balance sheet.
However, TNW provides information about the financial base of the client. As a lender (a deferred payment granted to the client equals a credit given), we must ask ourselves the following question: how much can I loan to this company?
TNW plays a pivotal role in the answer to this question: it does not make sense to give to the customer a credit limit greater than 100% of his TNW. 80% is far too high.
 Tip: Never set a credit limit exceeding 50% of the TNW, which is already very high.
Tip: Never set a credit limit exceeding 50% of the TNW, which is already very high.Every company has to define a rule that will serve as a benchmark in determining the credit limit. The calculator of credit limits developed by Credit tools weighted the "authorized %" of TNW to define credit limits based on several additional criteria.
This percentage varies depending on cases. For example, if the customer analyzed has serious cash flow problems, it is very risky to grant him an outstanding equal to 50% of its TNW because you may become his main creditor. You won't be able to disengage and you will face an agonizing dilemma:
This percentage varies depending on cases. For example, if the customer analyzed has serious cash flow problems, it is very risky to grant him an outstanding equal to 50% of its TNW because you may become his main creditor. You won't be able to disengage and you will face an agonizing dilemma:
- Cancel or reduce the credit line, which can push the customer to bankruptcy, which will result in bad debts for the supplier,
- Continue to accompany him by accepting late payments with the risk that despite this assistance he fills for bankruptcy and thus generates very large outstanding for those who have given support.

No comments:
Post a Comment